Bottom Feeder: Tench (Tinca tinca)
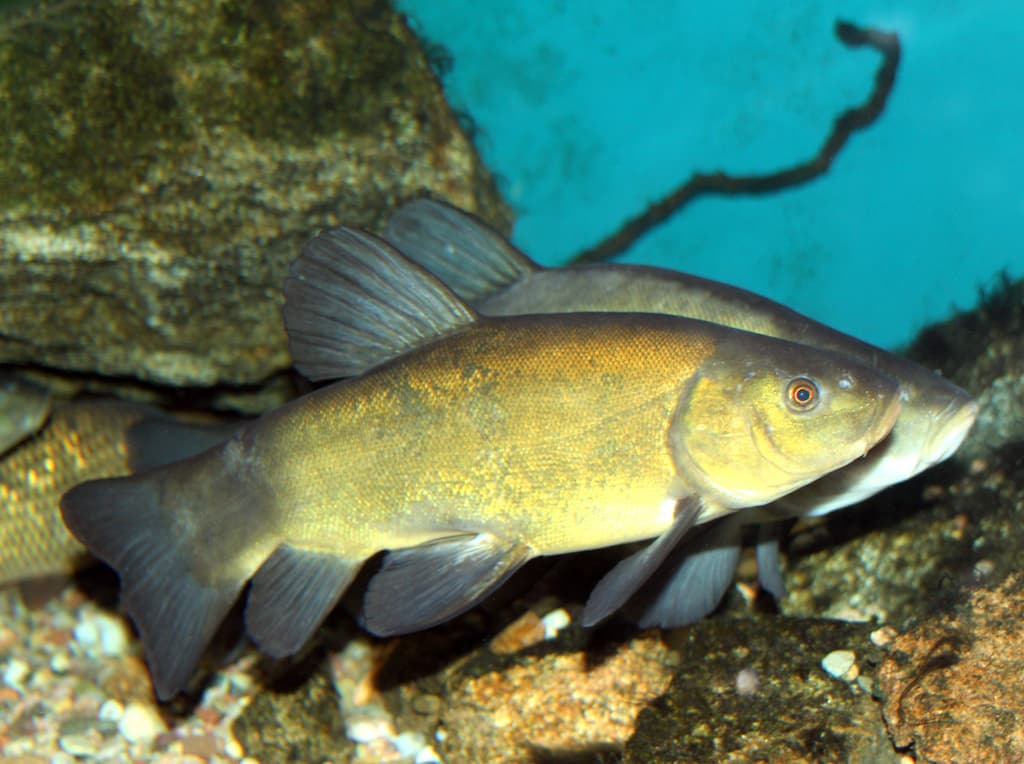

In the realm of freshwater fishing, the Tench (Tinca tinca) stands out as an intriguing species.
Known as a bottom feeder, this fish possesses unique characteristics that make it an exciting target for anglers. In this article, we will delve into the world of the Tench, exploring its description, size, habitat, lifespan, diet, and its significance in the wild and for anglers. Furthermore, we will provide valuable insights into effective fishing techniques for catching Tench. Let’s dive in and explore the captivating world of this remarkable fish.
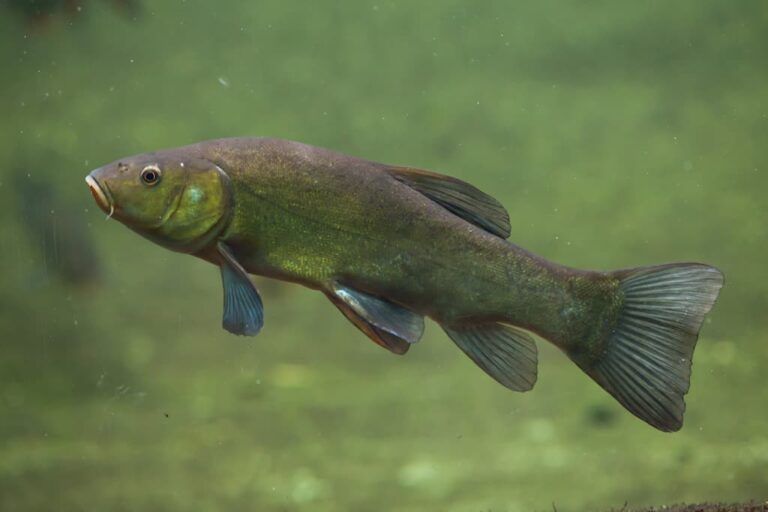

What is a Tench (Tinca tinca)?
Tench (Tinca tinca) is a bottom feeder fish with a unique body and lifestyle. This fish is characterised by a large head, powerful mouth and jaws, and distinctive olive-green or brownish body color. Tench is Found in freshwater bodies across Europe and Western Asia.
Description of a Fish: Tench (Tinca tinca)
Determination
The Tench boasts a robust body with an elongated shape. Its head is relatively large, displaying distinct features that set it apart. The fish’s mouth and jaws are positioned beneath its snout, equipped with powerful muscles for feeding and suction. Its eyes, located on either side of the head, provide excellent vision and aid in detecting prey.
The Tench’s fins are well-developed, consisting of dorsal, anal, and pelvic fins. These fins provide stability and control during swimming and maneuvering. The fish’s size varies, typically ranging from 10 to 16 inches in length, although some specimens can grow even larger. Its coloration is notable, with a dark olive-green or brownish hue covering its body.
| Class |
| Actinopterygii |
| Order |
| Cypriniformes |
| Family |
| Cyprinidae |
| Genus |
| Tinca |
| Species |
| T. tinca |
| Binomial Name |
| Tinca tinca (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Size and Weight
When it comes to size and weight, the Tench commonly reaches lengths between 10 to 16 inches and weighs around 2 to 5 pounds. However, exceptional individuals have been recorded, surpassing these average figures.
Lifespan
In the wild, the Tench can live for up to 10 to 15 years. However, under optimal conditions in domestic environments, their lifespan can extend beyond 20 years.
Habitat and Lifestyle of Tench (Tinca tinca)
Habitat
The Tench is primarily found in freshwater bodies across Europe and Western Asia. It prefers still or slow-moving waters such as lakes, ponds, and canals.
This species thrives in waters with dense vegetation and muddy bottoms, where it can find ample food and shelter.
Diet
Tench are omnivorous bottom feeders, feeding on a variety of aquatic organisms. Their diet includes insects, larvae, snails, worms, small crustaceans, and plant matter. This versatile feeding behavior contributes to their adaptability and widespread distribution.
Reproduction
Tench reproduce through external fertilization, with spawning occurring during the spring and early summer months. Female Tench release thousands of eggs, which are then fertilized by the males.
The eggs typically adhere to vegetation or other surfaces until they hatch. The young Tench grow rapidly, reaching maturity within a few years.
Importance of Tench
The Tench plays a vital role in the ecosystem as a bottom feeder. It helps maintain a healthy balance by consuming excess vegetation, controlling invertebrate populations, and serving as prey for larger predatory fish.
Although not commonly sought for food, the Tench holds great importance for anglers. Its challenging nature and strong resistance make it a prized catch, attracting fishing enthusiasts worldwide.
Fishing Techniques for Tench (Tinca tinca)
To successfully target Tench, anglers employ various techniques.
Bottom fishing with baits such as worms, maggots, or corn is a popular approach. Using specialized Tench rigs, which incorporate a float or feeder, can increase the chances of a successful catch.
Locating areas with dense vegetation and mud bottoms, where Tench typically reside, is essential. Patience, precision, and adapting to the Tench’s behavior are key factors in achieving angling success.
Common names for Tench
Most popular common names for the Tench are Tanche (french), Schleie (german), Tinca (italian), Tenca (spanish), Zeelt (dutch) and Lin (polish).
Conservation Status of the Tench (Tinca tinca)
Tench is classified as LC (Least Concern) in the IUCN Red List. This category corresponds to a species that is widespread and abundant.