Degradation Of Freshwater Aquatic Environment And Their Impact On Fishing
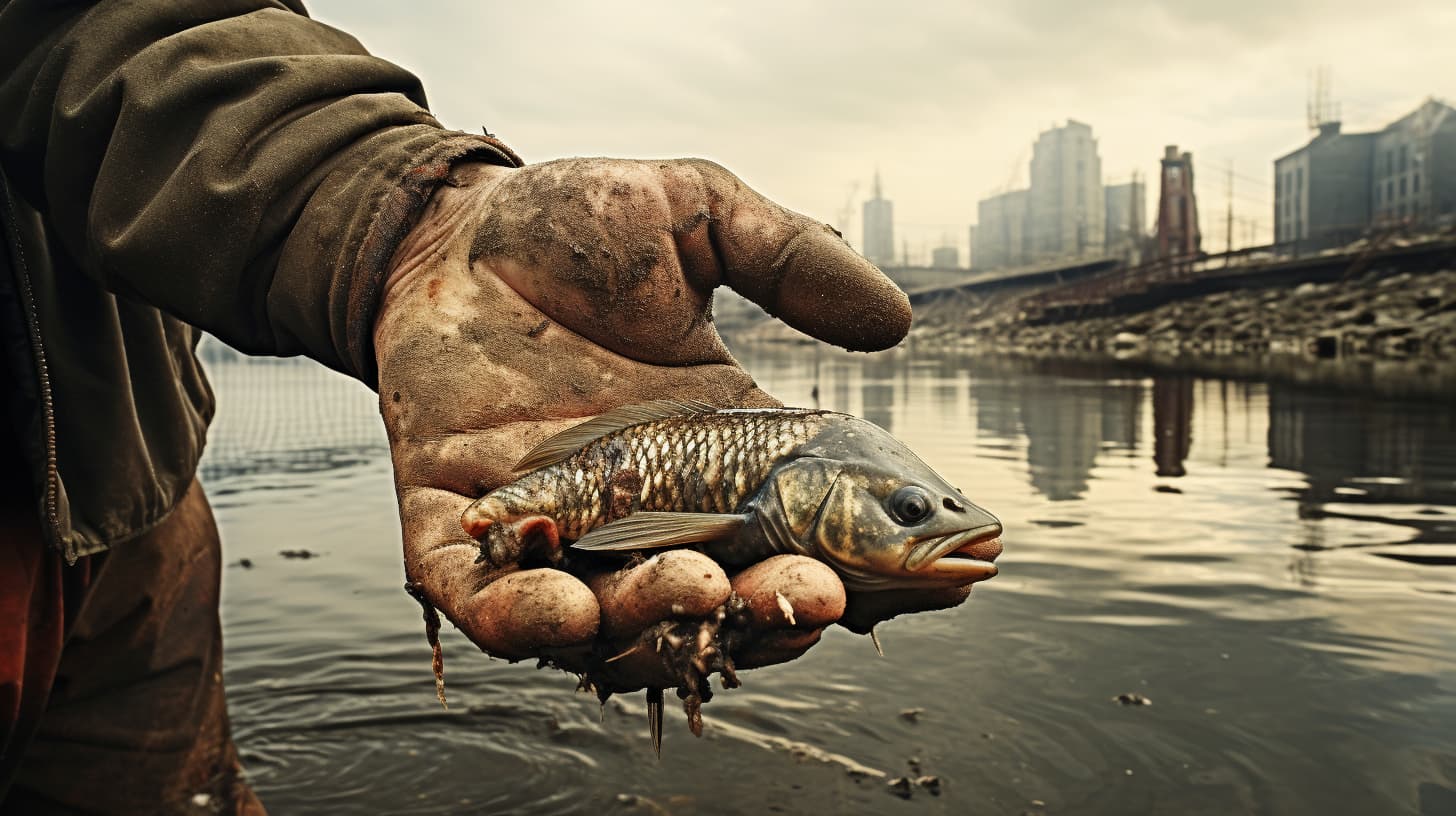

The health of our rivers and lakes is under threat, affecting both fish and those who rely on them. Pollution alone has put almost half of our freshwater fish at risk.
Our post explores the causes of this decline and how it impacts fishing communities.

Key Takeaways
- Pollution from industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and domestic sewage harm fish and disrupt freshwater ecosystems, posing a threat to fishing communities’ livelihoods.
- Destruction of wetlands and soil erosion contributes to the decline in fish populations by removing vital breeding grounds and disrupting natural habitats.
- Climate change – induced warming water, ocean acidification, variations in precipitation impact fish habitats and populations leading to a decline in aquatic biodiversity.
Causes of Freshwater Degradation
Industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and domestic sewage all contribute to pollution in freshwater environments.
Pollution from industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and domestic sewage
Factories dump chemicals and waste into rivers and lakes, harming fish and other aquatic life. Heavy metals like mercury can build up in the bodies of fish, making them unsafe to eat.
High levels of toxic substances from industrial runoff can lead to fish kills, where large numbers of fish die at once.
Agricultural activities release pesticides and fertilizers into waterways. These chemicals cause algal blooms that suck up oxygen, leaving little for the fish. Domestic sewage adds bacteria and viruses to the mix, further degrading water quality.
This pollution disrupts food webs in ponds and streams, posing a threat to freshwater ecosystems vital for fishing communities.
Soil erosion and wetland destruction
Soil erosion washes away the rich top layer of soil, often spilling it into nearby rivers and lakes. This sediment can cloud the water, making it difficult for fish to find food and breathe.
It also smothers plants that young fish need for shelter. Without these plants, there are fewer safe places for fish to lay their eggs or hide from predators.
Wetlands act as nature’s water filters, trapping pollutants before they reach open waters. They provide vital breeding grounds for many fish species which anglers cherish. Destroying wetlands means removing these crucial nurseries from aquatic ecosystems – a loss that leads to fewer fish in our rivers and lakes.
Ensuring the health of these habitats is essential not just for wildlife but also for maintaining successful fisheries.
Uncontrolled urbanization and industrialization
Cities are expanding rapidly, and industries are growing at an unprecedented pace. This relentless urbanization and industrial development have dire consequences for local rivers, lakes, and streams.
As concrete spreads across landscapes, it disrupts natural water drainage systems, leading to increased stormwater runoff that carries pollutants into freshwater habitats. Industrial effluents containing heavy metals, oils, chemicals, and other toxic substances further poison vital waterways.
Fishing communities feel the brunt of this degradation acutely. Fish populations decline due to polluted waters; many species can’t survive in these altered conditions. The environment suffers as biodiversity dwindles and previously thriving ecosystems become unbalanced or collapse entirely.
Excessive groundwater extraction by industries amplifies these issues by lowering water tables and reducing the volume of water available for fish to thrive in their natural habitats.
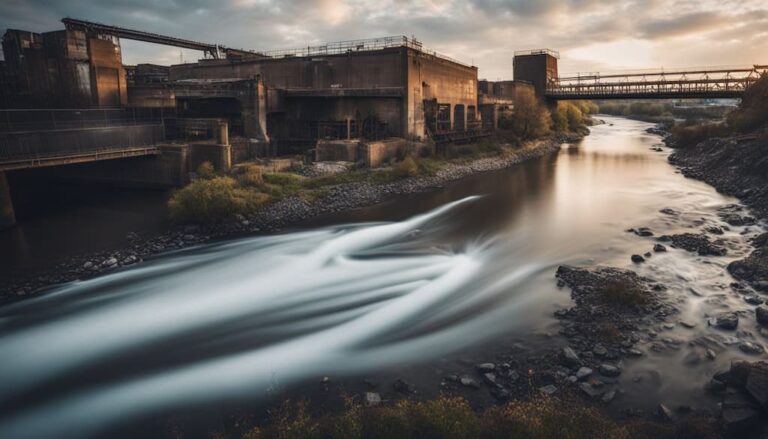

Impact of Freshwater Degradation on Fishing
Freshwater degradation poses a threat to aquatic biodiversity, endangers fish species like salmon, pike, and sturgeon, and disrupts aquatic ecosystems.
Threat to aquatic biodiversity
Pollution and habitat destruction are slicing through aquatic biodiversity like a knife. Industrial waste, agricultural run-off, and untreated sewage pour into rivers and lakes around the globe.
This toxic brew is deadly for many aquatic species. Fish such as salmon, pike, and sturgeon face dire threats; their numbers dwindle as their environments become unlivable.
Wetlands, once teeming with life, are being wiped out to make way for development—crucial spawning grounds lost in the blink of an eye. As these vital habitats vanish, so does the intricate web of life that depends on them.
The loss of biodiversity not only impacts species populations but also undermines the resilience of entire ecosystems upon which both fishers and anglers rely heavily for their livelihoods.
Endangerment of fish species like salmon, pike, and sturgeon
Salmon, pike, and sturgeon populations are plummeting due to human activities that degrade their freshwater habitats. Overfishing, disruption of spawning grounds, and barriers like dams interrupt these fish’s life cycles.
Salmon numbers drop as illegal fishing continues and vital river systems suffer from contamination with agricultural runoff loaded with nitrogenous and phosphate fertilizers.
Sturgeon face a dire future as well; they’re particularly vulnerable because they mature slowly and reproduce infrequently. Industrial wastewater releases heavy metals into the waterways where sturgeon live, causing lethal pollution levels for these ancient species.
Plastic debris also poses a threat by entangling marine life or being ingested. Ecosystems once teeming with diverse fish stocks are now facing critical imbalance as key species inch towards extinction.
Disruption of aquatic ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems face severe disruptions that can ripple through the entire food chain, affecting not just fish but also the fishermen and communities depending on them. Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff loaded with chemicals, and unchecked deposits of microplastics poison vital waterways.
These pollutants create toxic environments where marine life struggles to survive. Algal blooms, exacerbated by nutrient enrichment from fertilizers leaching into rivers, consume oxygen in the water until there’s little left for fish.
This process creates hypoxic dead zones where once thriving species like pike and sturgeon can no longer exist.
Destructive fishing techniques further damage delicate underwater habitats. Trawlers drag heavy nets across the seabed, disrupting not only the targeted species but also destroying homes of planktivorous fishes and other marine creatures integral to a balanced ecosystem.
Overfishing leads to biomass reduction which destabilizes food webs within aquatic systems; predatory fish lose their prey while smaller species grow unnaturally abundant without natural checks and balances in place.
All of these unhealthy changes make it tougher for fisheries to yield sustainable catches—hurting livelihoods along with wildlife—and challenge fishery management efforts aiming for conservation and restoration of our precious freshwater resources.
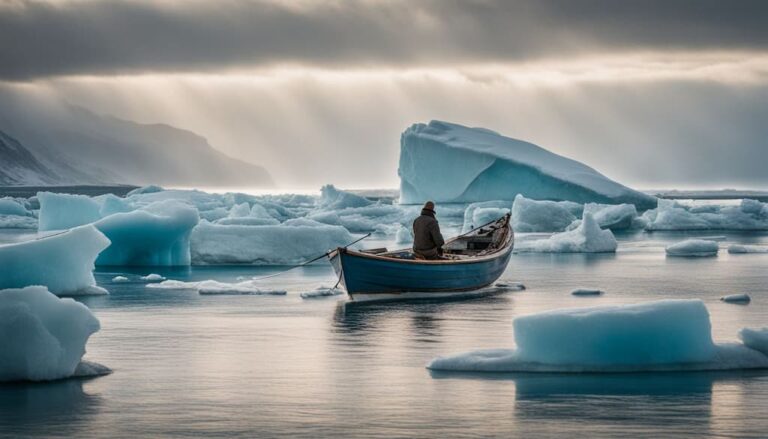

Effects of Climate Change on Aquatic Ecosystems
Climate change has led to warming water and ocean acidification, affecting fish habitats and populations. Read more about the impact of climate change on freshwater ecosystems and fishing practices.
Warming water and ocean acidification
Warming waters are shifting the conditions of aquatic habitats, which can cause stress on fish populations and affect their health. As water temperatures rise, certain species may struggle to survive, altering the dynamics of ecosystems and potentially leading to a decline in fish that anglers rely upon.
This also makes fish more susceptible to diseases and parasites that thrive in warmer conditions.
Ocean acidification is another troubling consequence of climate change where excess carbon dioxide lowers the pH levels of seawater. This creates a harsh environment for marine life, especially shellfish and coral reefs that need calcium carbonate to maintain their skeletons and structures.
It disrupts food chains too, impacting everything from tiny plankton to large marine mammals – all vital components of thriving marine ecosystems essential for productive fisheries.
Variations in precipitation
Variations in precipitation directly impact the availability of freshwater for fish and other aquatic organisms. Changes in rainfall patterns can lead to fluctuations in water levels, affecting the habitats of various fish species.
Excessive or inadequate precipitation can disrupt spawning grounds and migration routes, ultimately impacting the population dynamics of freshwater fish.
Notably, climate change is a significant driver of variations in precipitation. As global temperatures rise, weather patterns become more unpredictable, leading to extreme events such as heavy rainfall or droughts.
Impact on fish habitats and populations
Climate change has a direct impact on fish habitats and populations. Warming water temperatures alter the natural environment where fish live, affecting their breeding, feeding, and migration patterns.
Ocean acidification further poses a threat to fish populations by impacting their health and survival. Additionally, variations in precipitation can lead to changes in water flow and availability, further disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
The degradation of freshwater habitats significantly affects fish populations. Increased water temperatures, ocean acidification, and other climate-related factors pose significant challenges for various fish species’ survival.
Measures for Freshwater Conservation
Implementing strict regulations and laws to control pollution, promoting responsible fishing practices, and supporting freshwater conservation projects are essential measures for preserving and protecting the freshwater aquatic environment.
Implementation of regulations and laws
Regulations and laws play a vital role in maintaining the balance of fish populations. Minimum size laws and fishing quotas are crucial for preventing overexploitation, ensuring that fish have sufficient time to reproduce and maintain healthy population levels.
Additionally, periods of fishing closure during critical reproductive or growth periods are necessary to protect fish populations. Some countries also require a valid fishing permit to regulate and monitor fishing activities, thus contributing to sustainable fishing practices.
Designating protected areas where fishing is limited or prohibited is essential for preserving fish populations and their habitats. These measures help safeguard vulnerable species from extinction while ensuring the long-term sustainability of fisheries.
Responsible fishing practices
Fishers and anglers play a critical role in the preservation of freshwater ecosystems through responsible fishing practices. By respecting quotas and adhering to regulations, fishers can help maintain sustainable fish populations for future generations.
Techniques such as line fishing are recommended to minimize the impact on fish and their habitats. Additionally, supporting conservation efforts by participating in awareness initiatives and freshwater preservation projects is crucial for the long-term health of aquatic environments.
Furthermore, it is essential for fishers to be mindful of minimum fish size laws, periods of fishing closure, and requirements for valid fishing permits. By following these guidelines, they contribute significantly to the protection and sustainability of freshwater ecosystems.
Support for freshwater conservation projects
Funding for projects that aim to restore damaged aquatic ecosystems and protect essential fish habitats is crucial for supporting freshwater conservation. These projects focus on initiatives such as wetland restoration, pollution control, and the creation of protected areas, all of which are vital in preserving healthy freshwater environments for fish species.
Agencies have also implemented regulations to monitor and control industrial activities that may harm freshwater ecosystems, contributing to the success of these conservation efforts.
Public awareness about the importance of freshwater conservation plays a significant role in garnering support for these projects. By understanding the impact of degradation on fish populations, individuals can advocate for responsible fishing practices and contribute to the overall effort to protect our vital water resources.
Conclusion
Preserving freshwater ecosystems is crucial for maintaining healthy aquatic biodiversity and sustaining fish populations. Implementing regulations, promoting responsible fishing practices, and supporting conservation projects are essential steps towards freshwater conservation.
It’s imperative to address pollution, climate change, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems to safeguard the future of fishing and maintain a healthy environment for all aquatic life.